Many people suffer from lower back pain. Back pain is so common as the majority of activities we perform throughout our day involve activation of the lower back muscles. Back pain can be caused by poor posture, lack of core strength, improper lifting technique, and muscle weakness. Most of the time, physical therapy can help to decrease your lower back pain and get you back to your daily activities. However, if your back pain is too severe and physical therapy does not seem to help, the next step is to consult with an orthopedic surgeon who will most likely refer you for imaging to determine if there is an underlying condition at your spine causing the majority of your back pain. A physical therapist will help you to be able to navigate your treatment path to achieve the most optimal result.
back pain
Why Does my Back Hurt?
Many patients come to physical therapy with back pain. They come in asking the question, “why does my back hurt?” Well, the answer is not the same for everyone. A physical therapist has to perform a thorough evaluation to determine the cause of the patient’s back pain. The evaluation consists of finding out specific details from the patient about their back pain. This leads the therapist into a specific evaluation of the patient’s range of motion, strength, flexibility, and stability. Typically back pain comes from a lack of mobility, strength, and flexibility. For some patients, it is more of a decrease in flexibility, for others because of strength deficits, and some folks it is a combination of both. Once this is determined, your therapist will develop a plan of care to improve upon the deficits found during your evaluation. On average, it takes 4-6 weeks of consistent physical therapy to achieve the ultimate goal of decreased pain and improved function. The key as a patient is to be patient and stick with the plan. If after a month of physical therapy you do not notice any improvements, make sure to speak with your physical therapist to determine the appropriate continued treatment plan.
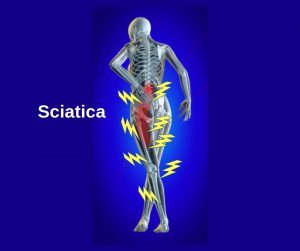
Common Causes of Sciatica
What is sciatica?
Sciatica is a term commonly used to describe pain, weakness, numbness, or tingling that radiates down the back of the leg. These symptoms can be debilitating for some and contribute to difficulty performing daily activities.
Where does it come from?
There are 4 common causes of sciatica:
- Disc Herniation – Pressure on the sciatic nerve can occur from the protrusion of a disc in the lumbar spine. This pressure can cause pain to travel through the pathway of the sciatic nerve down the leg.
- Spinal Stenosis – Narrowing of the space where the nerve roots exit the spinal canal can also cause pressure on the nerve.
- Piriformis Syndrome – The piriformis is a muscle deep in your gluteal region that the sciatic nerve runs underneath and sometimes through. Tightness or spasm of this muscle can cause pressure on the nerve that sends pain down the leg.
- Referred Pain from Trigger Points – Trigger points are tight knots in muscles that can cause local or referred pain. Trigger points found in the gluteal muscles can cause referred pain that is felt down the leg and is similar to sciatic nerve pain.
How can PT help?
A physical therapist is trained to evaluate your symptoms and do a thorough assessment to determine what may be causing them. The aim of treatment is to restore your range of motion, increase your flexibility, increase strength and stability, decrease trigger point formation, and improve your functional mobility. Treatment plans are individualized and are determined based on the causes of your symptoms and your specific presentation. If you are suffering from sciatica-related symptoms, call Harbor Physical Therapy to help eliminate your pain and prevent it from reoccurring.
Written by:
Dr, David Reymann
Staff Physical Therapist at Harbor Physical Therapy
4 Simple Exercises to Prevent and Treat Low Back Pain
1. Bridges
Lie on your back with you knees bent. While maintaining a neutral spine, lift your hips off of the ground and squeeze your glutes. This exercise well help you to build core and glute strength for increased lumbar stability.

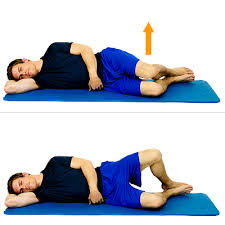
2. Clams
Lie on your side with your knees bent and feet together. Slowly raise your knee up without letting your hips roll forward or backwards. This exercise will help to build strength in your gluteus medius, which is important for stabilizing the hip and allowing you to have better control of the trunk and low back. Progress the exercise by placing a resistance band around the knees.
3. Lower Trunk Rotation
Lie on your back with your knees bent so that your feet are flat. Rotate your legs to the side while keeping your shoulders flat against the ground until a stretch is felt in your lower back. Hold for 10-20 seconds. Repeat to the opposite side. This is a good exercise to improve lower back flexibility.
4. Cat/Camel
While on your hands and knees, alternate between arching your back up and down. Hold for about 10 seconds each time. Just like the lower trunk rotation, this is another exercise that can help to improve low back mobility and decrease stiffness.
**These exercises may not be suitable for you if they worsen your symptoms or are too difficult for you to perform. It is recommended to seek out the expertise of a physical therapist if you are suffering from low back pain to provide you with exercises that are appropriate for your specific condition. Please contact Harbor Physical Therapy for further assistance**
Written by: Dr. David Reymann
Herniated Disc- Definition and Symptoms
A herniated disc is a condition in which the tough outer wall of an intervertebral disc (a soft cushion that sits between each vertabrae of the spine) has been weakened. The herniation causes the cushion that sits between the vertebra to be pushed outside its normal position.
A herniated disc commonly occurs in the low back and sometimes in the neck. Very seldom do they occur in the mid-back due to the extra stability provided by the rib cage. In some cases, a herniated disc will press against the spinal nerves, causing pain, numbness, tingling, or muscle weakness.
Pain
Pressure on the nerve can cause abnormal sensations, commonly experienced as electric shock pains. Compression in the neck region causes pain down your arms and compression in the low back region causes pain down your legs.
Tingling & Numbness
You might experience sensations such as tingling, numbness, or pins and needles. These symptoms may be experienced in the same region as painful sensations.
Muscle Weakness
Because of the nerve irritation, signals from the brain may be interrupted causing muscle weakness. Nerve irritation can also be tested by examining reflexes or having your doctor perform an EMG test. An EMG test is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles.
Bowel or Bladder Problems
These symptoms are important because it may be a sign of Cauda Equina syndrome, a possible condition resulting from a herniated disc. This is a medical emergency! See your doctor immediately if you have problems urinating, having bowel movements, or if you have numbness around your genitals.
If you experience any of these symptoms listed above, contact your physician or physical therapist to determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Avoiding Back Pain While Cooking Thanksgiving Dinner
Cooking for long periods of time can take a toll on your back. Here are some tips you can use to safely prepare your Thanksgiving meal without developing back pain.
When lifting the turkey, hold the pan close to your body as you take it to the oven. Bend at your knees, not at your lower back, as you lower it onto the oven rack. When taking the turkey out, bend at your knees and pull the rack out keeping your back straight while lifting the turkey out. Keep the turkey close to you. Pivot your feet without twisting your back, to bring the turkey to the counter top.
While peeling potatoes or slicing vegetables, you can prevent your back from hurting by either sitting down or by opening a lower cabinet door and setting one foot on the shelf. This takes weight off the back and prevents you from leaning forward as you work at the counter.
When you are cleaning up after your meal and putting things into the dishwasher, limit bending forward. Kneel down and have someone hand you the dirty dishes, or bend at the knees and keep your back straight while lowering plates to the bottom rack.
Can stress lead to pain?
Are you wondering if your back or neck pain can be related to stress? Many times stress alone can cause pain and if your spinal nerves are already irritated due to a previous injury, degenerative changes or scar tissue, it may only take a little extra muscle tension to increase your pain.
Stress creates muscle tension. This can cause compression to the nerves that run through your muscles. The compression of the nerves can result in symptoms such as aching, numbness, tingling, and sharp pains. Muscle tension reduces blood flow through the tissues robbing them of nutrients and oxygen. Sciatica is one of the most common problems that can be worsened with stress.
Try to manage your stress with techniques such as meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, guided imagery, massage therapy, walking or warm baths. Also, see your physical therapist as soon as your symptoms worsen. Physical Therapy will provide you with exercises and manual techniques to reduce muscle tension.
Back Pain and Physical Therapy
An episode of back pain can last anywhere from 2 to 8 weeks. Seeing a physical therapist can decrease your healing time and prevent further injury.
Typical treatment will consist of heat or cold packs, electrical stimulation, ultrasound, massage, stretching, postural education, and lumbar stabilization exercises.
Stretching exercises are performed to restore your flexibility and motion. Strengthening exercises are performed to increase the muscular support of your spine to prevent further injury.
Tips to Prevent A Back Injury While Gardening
As spring and summer are approaching, we begin to get back to our gardening. While gardening, many people develop back injuries due to improper body mechanics. Therefore, listed below are tips to decrease the likelihood of a back injury this gardening season.
- Before gardening, take a 10 minute walk or warm up with some light exercises to warm up your muscles.
- While shoveling, remember to bend at your knees and hips, not at your waist.
- When you empty a shovel full of mulch or dirt, make sure you pivot your feet while turning your upper body.
- Sit or kneel on a small stool or bucket while weeding and planting so you are not bending over. Use knee pads to kneel to avoid pressure on your knees.
- Switch jobs every 30 minutes and take a break every 15 minutes.
- Working on raised beds is less strenuous for your back because you are not bending over as much.
- Use a cart or wheelbarrow to move things.
- Use lightweight hoses for watering.
- Keeps loads light. Buy smaller bags of dirt and mulch. They might be more costly but they will save your back.
- Use ergonomic tools for pruning and planting. Buy long handled tools so you don’t have to reach as far.
- Keep your body straight and get under the wheelbarrow to tilt it. Stand straight while emptying the wheelbarrow.
- While mowing the lawn, keep a comfortable distance between your hands and your body.
- If you experience any pain while doing lawn work or gardening, stop.
- Do gentle stretches when you are finished gardening to prevent tightness/pain the following day.
Auto Accident Injury, Do I see a Physical Therapist or a Chiropractor
After an auto accident, it is common to sustain an acute injury to your muscles. An acute injury has a rapid onset and involves an inflammatory process of the soft tissues. Soft tissue injuries consist of the muscles, fascia, and tendons. A neck and back injury is the most common injury sustained from an auto accident.
For an acute injury, it is best to visit your local physical therapist because therapists are trained to rehabilitate injured muscle in a conservative manner. After an auto accident, physical therapy focuses on decreasing muscle tightness and inflammation, which is ultimately causing pain and decreasing function.
If you have tried physical therapy for approximately 6 weeks and have not seen any results, it is recommended you contact your physician. Your physician might at that point suggest seeking chiropractic care and or imaging tests. After an auto accident, most people receive positive results with approximately 6 weeks of physical therapy.